你不可或缺的晶亮元素~葉黃素
張珮蓁營養師 Dietitian Patty
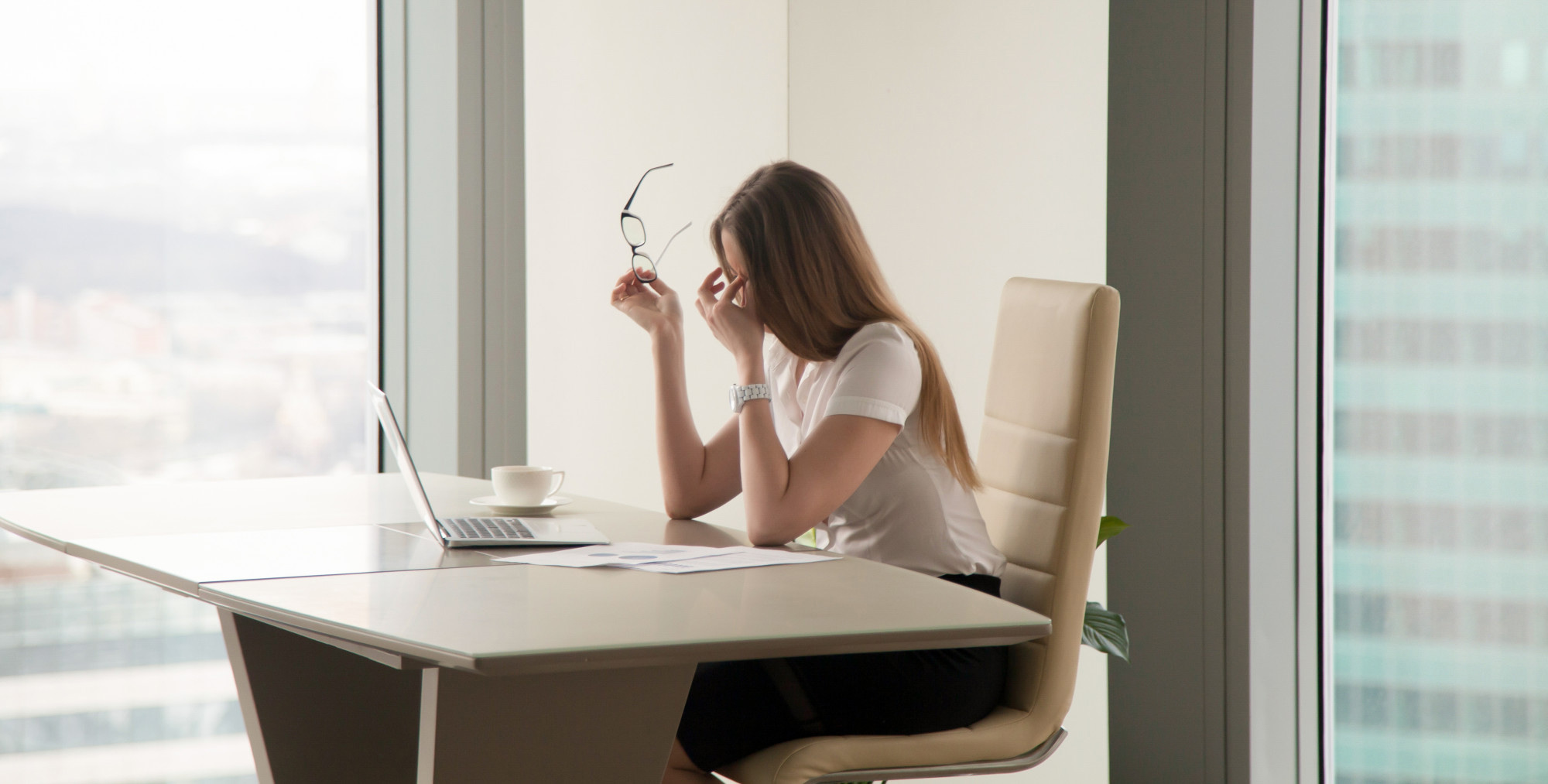
在 3C 的時代,現代人除了工作需求外,就連空閒娛樂也很常離不開電子產品。導致眼睛無法適當的休息,長時間持續不斷的挑戰眼睛的極限,除了帶來了疲勞外,還會增加眼睛病變罹患率,如黃斑部病變等問題。

- 葉黃素是什麼?
- 葉黃素食物來源為何?
- 葉黃素的保健好處?
- 降低藍光傷害增強保護力
- 減少老年性黃斑罹患率
- 有助於降低患心血管疾病的風險
- 與輔助改善認知功能有關
- 怎麼補充?要補充多少?

葉黃素是什麼?
葉黃素(Lutein)為脂溶性類胡蘿蔔素的其中一種,為黃斑部的重要營養來源,具有吸收光線、過濾藍光等功能。而黃斑部在視網膜的正中心,含有黃色色素,所以被稱為黃斑部,是我們眼睛辨色、光度等精細工作最敏銳的部位。
而葉黃素在自然界中常與玉米黃素(Zeaxanthin)一同存在,要達到全方位護眼,兩者缺一不可1。
葉黃素食物來源為何?
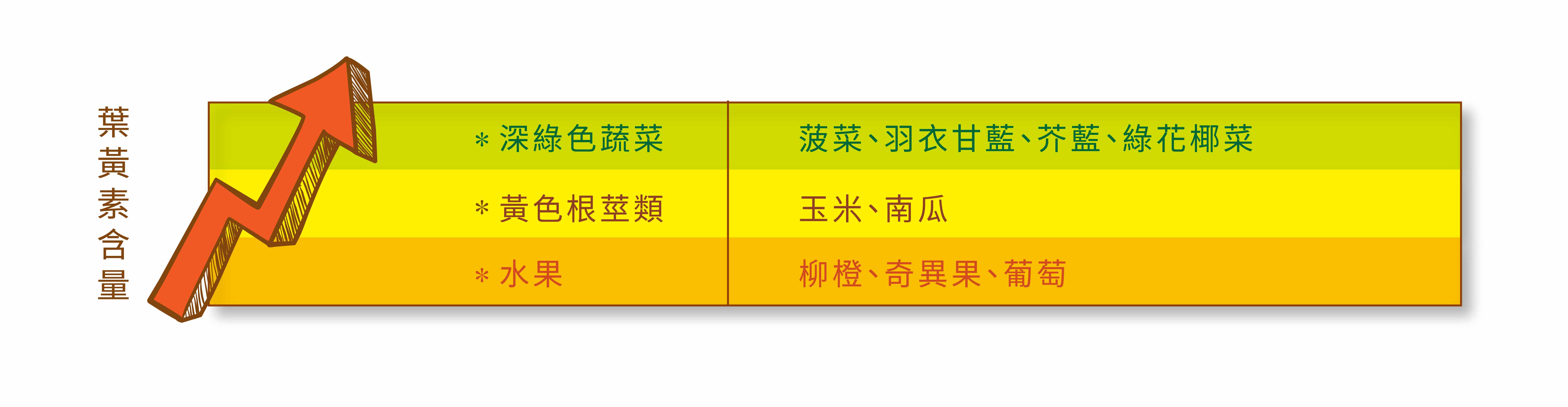
葉黃素的保健好處?
- 降低藍光傷害增強保護力
- 預防退化性黃斑部病變 (AMD)
- 有助於降低患心血管疾病的風險
- 與輔助改善認知功能有關
研究發現靈長類動物的視網膜中葉黃素濃度(即黃斑色素密度)與腦中濃度有關,且與成人的認知功能有關,因此成人補充葉黃素可輔助改善認知功能7,8。

- 葉黃素為脂溶性維生素,建議隨餐攝取搭配餐食中的油質一同攝取,吸收較佳。
- 依劑型分為游離型與酯化型
酯化型:分子較大,生物利用率與安定性較好,但須透過腸道酵素輔助,若本身消化不好者較不建議使用。
- 不建議與 β-胡蘿蔔素補充品一起使用,因吸收途徑相同,避免產生競爭吸收,使得葉黃素吸收率下降。
- 與一般保健食品同,保健效果並不是立即,須連續使用 2 至 4 個月,才能顯著提升眼睛黃斑部的葉黃素濃度,達到抵禦藍光保護眼睛的效果。
- 根據美國食品藥品監督管理局(FDA)建議,每日葉黃素建議攝取量為 6 毫克(mg),而台灣食藥署建議不超過 30 毫克(mg),多食無益。
- 而標榜「葉黃素」補充劑的保健食品,葉黃素濃度要佔總類胡蘿蔔素含量 75% 以上,符合標準才能稱為「葉黃素」保健食品,若不足則只能稱為金盞花萃取物,因此挑選補充時應特別留意。

參考來源:
1.Li, L. H., Lee, J. C., Leung, H. H., Lam, W. C., Fu, Z., & Lo, A. (2020). Lutein Supplementation for Eye Diseases. Nutrients, 12(6), 1721.
2.Hammond, B. R., Johnson, B. A., & George, E. R. (2014). Oxidative photodegradation of ocular tissues: beneficial effects of filtering and exogenous antioxidants. Experimental eye research, 129, 135–150.
3. Karppi, J., Laukkanen, J. A., & Kurl, S. (2012). Plasma lutein and zeaxanthin and the risk of age-related nuclear cataract among the elderly Finnish population. The British journal of nutrition, 108(1), 148–154.
4.Junghans, A., Sies, H., & Stahl, W. (2001). Macular pigments lutein and zeaxanthin as blue light filters studied in liposomes. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics, 391(2), 160–164.
5. Alves-Rodrigues, A., & Shao, A. (2004). The science behind lutein. Toxicology letters, 150(1), 57–83.
6.Olmedilla-Alonso, B., Rodríguez-Rodríguez, E., Beltrán-de-Miguel, B., Sánchez-Prieto, M., & Estévez-Santiago, R. (2021). Changes in Lutein Status Markers (Serum and Faecal Concentrations, Macular Pigment) in Response to a Lutein-Rich Fruit or Vegetable (Three Pieces/Day) Dietary Intervention in Normolipemic Subjects. Nutrients, 13(10), 3614. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103614
7.Jia, Y. P., Sun, L., Yu, H. S., Liang, L. P., Li, W., Ding, H., Song, X. B., & Zhang, L. J. (2017). The Pharmacological Effects of Lutein and Zeaxanthin on Visual Disorders and Cognition Diseases. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland), 22(4), 610.
8.Johnson, E. J., McDonald, K., Caldarella, S. M., Chung, H. Y., Troen, A. M., & Snodderly, D. M. (2008). Cognitive findings of an exploratory trial of docosahexaenoic acid and lutein supplementation in older women. Nutritional neuroscience, 11(2), 75–83.

